Table of Contents
Lebanon’s insurance legal framework combines statute, administrative oversight, and contract law to define how insurers operate and how policyholders obtain and enforce coverage. This guide explains the foundation of Lebanon’s insurance regime naming Decree 9812/1968 and the Lebanese Code of Obligations and Contracts then maps those rules to practical obligations for individuals, expatriates, businesses, and insurers. Readers will learn which policies are regulated or compulsory, how the Insurance Control Commission (ICC) supervises solvency and licensing, and what dispute-resolution routes and consumer protections exist in practice. The article also compares regulated insurance types, summarizes licensing and capital expectations for insurers, and reviews market trends affecting coverage availability in 2025. Throughout, the focus is practical: clear definitions, stepwise compliance actions, and references to insurer solutions where relevant, helping policyholders and businesses make informed choices while staying compliant with Lebanon’s regulatory framework.
What Is the Legal Framework Governing Insurance in Lebanon?
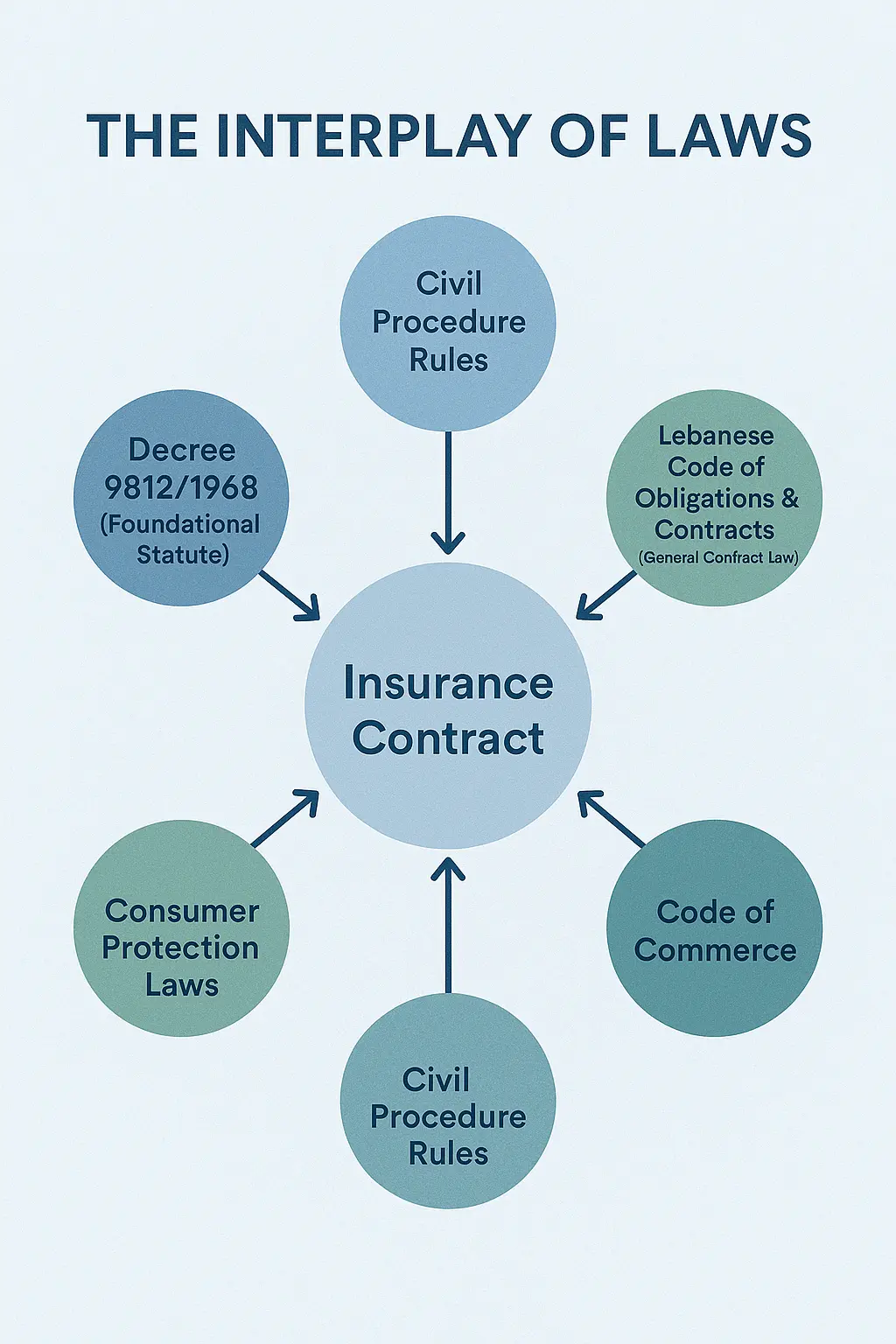
The legal framework governing insurance in Lebanon consists of primary insurance legislation, contract law, and complementary commercial and administrative rules that together regulate insurer conduct and policyholder rights. At its core sits Decree 9812/1968, which establishes licensing, supervisory powers, and certain insurer obligations, while the Lebanese Code of Obligations and Contracts provides general contract principles offer, acceptance, insurable interest, disclosure and subrogation that shape insurance agreements. These instruments interact with the Code of Commerce and consumer protection provisions to create an operational environment where regulatory oversight and private-contract rules work in tandem to govern premiums, claims handling, and contractual terms. Understanding this multi-layered framework helps policyholders evaluate policy validity and compliance, and it frames expectations for insurers and intermediaries operating in the Lebanese market.
What Is Decree 9812/1968 and How Does It Regulate Insurance?
Decree 9812/1968 is the foundational statute that addresses the organization and supervision of the insurance sector in Lebanon, setting out licensing prerequisites, oversight mechanisms, and the basic duties of insurers. The decree defines which activities require authorization, establishes supervisory competence for the Insurance Control Commission (ICC), and prescribes reporting and administrative requirements for licensed entities. Practically, the decree functions as the primary regulatory instrument that shapes market entry, ongoing supervision, and administrative enforcement actions against non-compliant insurers. Understanding its scope helps businesses and policyholders know where to look for formal regulatory obligations and which administrative remedies may be available when statutory duties are breached.
How Does the Lebanese Code of Obligations and Contracts Influence Insurance Contracts?
The Lebanese Code of Obligations and Contracts supplies the general contract law principles that insurance policies must respect, including rules on consent, disclosure, performance and remedies for breach. In insurance contexts, these principles translate into specific doctrines such as insurable interest, utmost good faith obligations, pre-contractual disclosures, indemnity principles, and subrogation rights that determine how claims are assessed and disputes decided. For policyholders, the Code means that standard commercial contract protections apply: representations must be accurate, material facts disclosed, and remedies follow civil-law patterns. Translating these contract doctrines into practice clarifies expectations during underwriting and claims handling and provides policyholders with predictable legal remedies when disputes arise.
Which Other Laws Affect Insurance Regulation in Lebanon?
Several laws beyond primary insurance statutes influence how insurance is regulated and enforced, creating cross-cutting obligations for insurers and policyholders. The Code of Commerce governs certain commercial practices relevant to underwriting and brokerage, while civil procedure rules shape dispute timelines and evidentiary requirements in court. Consumer protection provisions impose disclosure and fair-treatment standards that affect policy wording and marketing, and tax rules influence premium pricing and the financial obligations of insurers. Recognizing this legal constellation helps stakeholders anticipate areas where different legal regimes intersect and where to seek authoritative guidance for sector-specific issues.
How Do These Laws Impact Individuals and Businesses?
These laws translate into concrete consequences for consumers and corporate buyers: they determine required disclosures at sale, define the enforceability of exclusions, and set procedural expectations for claims and litigation. For individuals, the framework requires accurate disclosure of material facts and offers legal remedies for denied claims; businesses face additional considerations around corporate policies, indemnity limits, and sectoral compliance for industries like shipping or aviation. Practically, both individuals and enterprises should review policy wording against statutory duties, maintain clear documentation for claims, and consult regulatory guidance when encountering unclear contract terms. These legal effects underscore the importance of aligning commercial insurance decisions with statutory and regulatory obligations.
What Is the Role of the Insurance Control Commission in Lebanon?
The Insurance Control Commission (ICC) is the primary supervisory body charged with authorizing insurers, monitoring solvency and capital adequacy, and enforcing compliance to protect policyholders and market stability. The ICC’s mandate includes licensing decisions, regular reporting requirements, on-site inspection power, and the authority to take administrative measures against firms that fail to meet regulatory standards. By supervising financial health and conduct, the ICC seeks to limit systemic risk, ensure insurers meet reserve and solvency obligations, and promote transparent market practices that protect policyholder interests. Understanding the ICC’s remit helps consumers identify the administrative routes for complaints and allows market participants to prepare for ongoing compliance and reporting responsibilities.
How Does the ICC Supervise and License Insurance Companies?

ICC licensing follows a structured application and assessment process that evaluates an applicant’s governance, capital adequacy, business plan, and reinsurance arrangements before authorization is granted. After licensing, supervision continues through periodic reporting, actuarial reserve reviews, audited financial statements, and potential on-site inspections to verify compliance with solvency and reserve rules. The ICC also monitors related-party transactions and corporate governance practices to ensure that licensees operate in a manner consistent with policyholder protection objectives. For potential entrants, preparing robust documentation and sound governance arrangements increases the likelihood of a timely licensing outcome and reduces regulatory friction during ongoing supervision.
What Are the ICC’s Responsibilities Regarding Solvency and Capital Requirements?
The ICC oversees minimum paid-up capital thresholds, technical reserves, and solvency margins that insurers must maintain to absorb losses and meet policyholder obligations. Supervisory measures include reviewing reserve calculations, requiring actuarial certifications, and intervening if capital falls below regulatory minima measures that can range from remedial plans to administrative sanctions. The ICC’s solvency oversight aims to preserve market confidence and minimize disruptions from insolvency events, and it often evolves in response to market conditions or systemic risk concerns. Insurers must therefore maintain transparent financial reporting and prudent reserve practices to remain compliant and to satisfy the ICC’s solvency expectations.
How Does the ICC Protect Policyholders and Ensure Consumer Rights?
ICC consumer-protection responsibilities include enforcing disclosure obligations, supervising claims-handling practices, and providing administrative recourse mechanisms for unresolved complaints against insurers. The Commission sets expectations for transparent policy terms, prompt claims processing, and fair treatment of policyholders; it can investigate complaints and require corrective measures when systemic issues are identified. Policyholders should document communications, follow insurer complaint procedures, and escalate unresolved matters to the ICC to invoke supervisory scrutiny. The ICC’s protective role complements judicial remedies and arbitration avenues, creating multiple pathways to resolve consumer disputes.
How Does the ICC Collaborate with the Ministry of Economy and Trade?
The ICC coordinates with the Ministry of Economy and Trade on regulatory policy, market oversight, and initiatives aimed at modernizing insurance legislation and supervisory practices. This collaboration can include joint technical work on draft regulations, market monitoring efforts, and policy responses to systemic challenges that affect economic stability. Coordinated oversight helps align sector regulation with broader economic policy priorities and can accelerate modernization measures when systemic or consumer protection concerns emerge. Such institutional cooperation supports coherent regulatory responses and strengthens the overall governance of the insurance sector.
What Types of Insurance Are Regulated Under Lebanese Law?
Lebanese law regulates a broad set of insurance categories life, health, motor, property, corporate liability, travel and expatriate insurance each subject to specific legal, underwriting, and disclosure requirements depending on risk profile and statutory mandates. Regulation addresses product authorization, permissible contract terms, solvency and reserve implications for insurers, and sector-specific obligations such as compulsory motor third-party liability coverage. Non-admitted cross-border insurance also receives regulatory attention due to solvency and consumer-protection concerns. The following table summarizes each insurance type’s legal status and primary regulatory considerations, providing a quick comparison for consumers and businesses evaluating coverage options.
Insurance Type | Legal Status | Key Notes |
|---|---|---|
Motor (third-party liability) | Compulsory | Mandatory for registered vehicles; primary public-safety focus |
Health (including expatriate) | Regulated; certain categories effectively required | Disclosure rules; employer/immigration-linked coverage considerations |
Life insurance | Regulated | Contract formalities and beneficiary protections apply |
Property insurance | Regulated | Insurer underwriting and documentation standards enforced |
Corporate liability insurance | Regulated | Often subject to sector-specific compliance (construction, industry) |
Travel insurance | Regulated | Standardized policy terms and consumer disclosure expectations |
Non-admitted insurance | Restricted/monitored | Cross-border use carries consumer risk; authorized insurers preferred |
This comparison helps stakeholders identify which cover types carry statutory obligations and which require careful contract scrutiny to ensure enforceability and compliance.
At The Guardian Insurance, we offer a range of solutions including Motor, Life, Health, Expatriate, Property, Corporate, and Travel insurance designed to help individuals and businesses meet these legal requirements and secure their future. Explore our product pages to find the coverage that’s right for you.
What Are the Legal Requirements for Life and Health Insurance in Lebanon?
Life and health insurance in Lebanon must conform to contract-law principles requiring clear policy wording, disclosure of material facts, and precise beneficiary and premium arrangements. For health coverage, regulators emphasize appropriate policy terms, exclusions, and disclosure standards that protect consumers and ensure transparent claims handling, while expatriate health coverage often involves additional immigration or employer-related compliance considerations. Insurers must maintain reserves consistent with actuarial standards for life and health lines to secure long-term policyholder obligations. Consumers should verify policy documentation, confirm the scope of benefits and exclusions, and retain complete records to facilitate claims or regulatory complaints when disputes arise.
How Is Motor Insurance Regulated, Including Compulsory Third-Party Liability?
Motor insurance is one of the most regulated spheres because compulsory motor third-party liability (TPL) protects third parties injured or harmed by vehicle operation and thus supports public safety objectives. Vehicle registration authorities typically require proof of TPL coverage before allowing registration or use, and penalties apply for non-compliance or driving without valid cover. Motor policies must clearly state limits, exclusions, and claims procedures, and insurers are required to process accident claims under defined administrative timeframes. Vehicle owners should maintain continuous coverage, carry proof of insurance when required, and follow statutory accident-reporting steps to preserve their rights and comply with enforcement obligations.
What Are the Rules for Property, Corporate, Travel, and Expatriate Insurance?
Property, corporate liability, travel and expatriate insurance categories each carry distinct regulatory considerations tied to underwriting practices, documentation, and sector-specific compliance obligations. Property insurance requires accurate valuation, disclosure of hazards, and clear statements of coverage and exclusions; corporate liability policies must align with statutory safety and indemnity rules for certain industries. Travel insurance needs transparent consumer disclosures about trip cancellation, medical evacuation and coverage limits, whereas expatriate insurance must address residency status and employer obligations where relevant. Buyers should review underwriting requirements, confirm required documentation, and consult sectoral rules to ensure that chosen policies meet regulatory expectations.
What Is Non-Admitted Insurance and How Is It Treated Legally?
Non-admitted insurance refers to coverage issued by an insurer not authorized in Lebanon and is treated with caution because it may lack local regulatory oversight and consumer protections. Using non-admitted policies can expose policyholders to enforcement risks, difficulties in claims enforcement, and reduced remedies if insolvency or disputes arise. Regulators generally prefer authorized insurers for consumer protection and solvency oversight, and stakeholders should seek clarity from the ICC or legal counsel before relying on cross-border arrangements. When non-admitted options are considered, buyers should document reasons for use, understand dispute-resolution mechanisms, and evaluate counterparty creditworthiness carefully.
Which Insurance Policies Are Compulsory in Lebanon and What Are Their Legal Obligations?
Certain insurance policies are compulsory under Lebanese law or administrative rules, most notably motor third-party liability, with additional sectoral requirements potentially applying to aviation, marine, or employer-related health coverage depending on regulatory rules. Compulsory policies carry precise compliance steps: valid documentation at registration, minimum cover expectations where specified, and administrative or criminal penalties for non-compliance in some contexts. This section clarifies who must maintain compulsory cover, how to verify compliance, and what enforcement mechanisms apply.
Compulsory Policy | Who Must Comply | Key Legal Obligations / Penalties |
|---|---|---|
Motor third-party liability | Registered vehicle owners/drivers | Maintain valid policy, present proof at registration; penalties for lapses apply |
Employer/immigration-linked health (where applicable) | Employers or foreign residents | Maintain required cover for employees or visa conditions; administrative sanctions possible |
Sectoral (aviation/marine/professional) | Regulated operators | Maintain sector-mandated covers and certifications; regulatory fines or operational restrictions |
To help you meet these statutory obligations, The Guardian Insurance offers essential Motor and Expatriate Health Insurance solutions. Explore our product pages or contact us to ensure your coverage aligns with legal requirements. Practical compliance advice includes verifying policy certificates at vehicle registration or employment onboarding and ensuring continuous cover to avoid enforcement action.
What Are the Requirements for Motor Third-Party Liability Insurance?
Motor third-party liability insurance requires vehicle owners to hold valid coverage that compensates third parties for bodily injury or property damage resulting from vehicle operation, ensuring public protection and financial responsibility. Proof of coverage is commonly required for registration and police inspections, and insurers must process TPL claims promptly in accordance with regulatory standards. After an accident, vehicle owners should document the scene, exchange information, and notify insurers within statutory timelines to preserve claim rights. Maintaining continuous TPL cover and understanding policy limits and exclusions are essential steps to comply with legal obligations and protect third-party interests.
Who Must Have Health Insurance Under Lebanese Law?
Health insurance obligations can apply to particular categories such as foreign residents, employees under certain employer arrangements, or individuals tied to administrative requirements, with precise thresholds and enforcement determined by relevant statutes or administrative rules. Employers should confirm whether employment contracts or immigration rules require specific health coverage for staff or expatriates and document that coverage as part of compliance checks. Individuals should verify coverage applicability during immigration or employment onboarding and maintain records that demonstrate continuous protection. When in doubt, consulting regulatory guidance or insurer documentation clarifies whether health coverage is statutorily required in a specific circumstance.
Are There Other Compulsory Insurance Types Like Aviation or Marine Liability?
Certain sectors aviation, marine, and professional services may be subject to compulsory insurance requirements imposed by sector regulators to protect third parties and preserve operational safety. These sector-specific obligations often arise from international conventions, safety regulations, or industry licensing conditions and require operators to maintain minimum covers such as hull, P&I, or professional indemnity insurance. Businesses operating in regulated sectors must consult sector regulators and ensure that their insurance programs meet mandated minimums to preserve licenses and avoid operational restrictions. Regulatory authorities and industry guidance are the appropriate sources for precise sectoral insurance thresholds.
How Does The Guardian Insurance Help Comply with These Compulsory Laws?
At The Guardian Insurance, we offer Motor and Expatriate Health Insurance plans specifically designed to help you comply with these compulsory laws. Explore our product pages or contact us directly to request tailored quotes and documentation that align with statutory obligations, ensuring you have the necessary certificates and policy schedules to demonstrate coverage to regulators and registration authorities.
How Are Insurance Companies Regulated in Lebanon Regarding Licensing, Capital, and Solvency?
Insurance companies in Lebanon must satisfy licensing criteria, maintain prescribed paid-up capital and technical reserves, and submit to ongoing solvency monitoring to protect policyholders and maintain market stability. Licensing evaluates governance, reinsurance arrangements, and business plans; capital and reserve requirements are calibrated to line of business and risk exposure; and solvency monitoring involves actuarial reviews and supervisory benchmarks used by the ICC. The following table summarizes common regulatory requirements and their applicability to insurers operating in Lebanon, offering a compact reference for corporate compliance planning.
Regulatory Requirement | Applies To | Minimum / Procedure / Effect |
|---|---|---|
Licensing documentation | Prospective insurers | Submit governance, capital plan, business plan; ICC evaluates before authorization |
Paid-up capital & reserves | Licensed insurers | Minimum thresholds set by ICC; shortfalls trigger remedial measures |
Solvency monitoring | All insurers | Periodic reporting, actuarial certification; supervision escalates if metrics deteriorate |
As a trusted insurer, The Guardian Insurance adheres strictly to ICC rules. Organizations seeking a legitimate and reliable partner can explore our About/Services pages to understand our corporate governance and commitment to excellence.
What Are the Licensing Procedures for Insurers in Lebanon?
Licensing procedures require applicants to prepare comprehensive documentation that demonstrates sound corporate governance, solvency plans, reinsurance arrangements, and a viable business model for the proposed insurance activity. The ICC reviews these submissions, may request supplementary information, and performs suitability assessments of shareholders and directors as part of the authorization decision. After licensing, firms must adhere to ongoing disclosure and reporting obligations to retain their authorization. Prospective entrants should anticipate iterative regulatory review and build robust governance and compliance frameworks to satisfy licensing expectations.
What Are the Minimum Capital and Reserve Requirements?
Minimum capital and reserving rules are designed to ensure insurers can meet policyholder liabilities and absorb adverse loss experience, and thresholds may be adjusted over time in response to market conditions or supervisory objectives. Regulators commonly require actuarial certification of technical reserves and may specify different paid-up capital minima by line of business. When capital or reserve shortfalls occur, supervisors may require recovery plans, capital injections, or other remedial measures to restore solvency. Maintaining prudent reserving practices and transparent financial reporting helps insurers remain compliant and reduces the probability of supervisory intervention.
How Does Foreign Direct Investment Affect Insurance Company Operations?
Foreign direct investment (FDI) can influence market entry routes, governance structures, and reinsurance access for international insurers operating in Lebanon; regulators may impose conditions to ensure local solvency and oversight. Foreign investors should evaluate local rules on ownership, reporting, and cross-border capital movements, and they must ensure that offshore reinsurance arrangements do not undermine local solvency safeguards. Practical implications include the need for clear reinsurance treaties, capital remittance planning, and compliance with ICC disclosure requirements when foreign backing is part of a license application. Proper structuring and regulatory engagement facilitate sustainable operations and market acceptance.
What Are the ICC’s Solvency and Risk Management Standards?
The ICC applies solvency standards that require insurers to measure technical reserves, maintain capital buffers, and implement risk management systems that address underwriting, credit, market and operational risks. Supervisory expectations include governance frameworks, internal controls, actuarial validation of reserves, and periodic risk reporting. Best-practice risk management includes stress testing, reinsurance strategies, and robust compliance functions to monitor emerging risks. Firms that adopt comprehensive risk management practices are better positioned to satisfy supervisory scrutiny and protect policyholder interests through prudent capital and reserve management.
How Are Insurance Disputes Resolved and What Consumer Protections Exist in Lebanon?
Insurance disputes in Lebanon can be resolved through administrative complaint channels, arbitration via the Insurance Arbitration Council (IAC), or litigation in Lebanese courts, with each route offering distinct procedural and enforcement characteristics. Consumer protections include disclosure rules, fair-treatment expectations, and avenues for regulatory complaint to the ICC. Policyholders should follow insurer complaint procedures, preserve documentation, and consider arbitration or court action where administrative remedies do not resolve substantive claim denials. The combination of administrative oversight, arbitration, and judicial review provides multiple mechanisms for dispute resolution, increasing avenues for policyholder redress.
What Is the Role of the Insurance Arbitration Council?
The Insurance Arbitration Council (IAC) provides a specialized forum for resolving disputes between insurers and policyholders or between insurers themselves, offering procedural efficiency and industry expertise. Arbitration before the IAC can be faster and more technical than general court litigation and typically results in awards enforceable under Lebanese law. Initiating arbitration requires adherence to procedural rules and often depends on arbitration clauses in policies or consent by parties. For many disputes especially technical coverage questions the IAC represents a practical alternative to lengthy court proceedings.
How Do Lebanese Courts Handle Insurance Disputes?
Lebanese courts adjudicate insurance disputes following civil procedure rules, requiring claimants to present documentary evidence, expert testimony where appropriate, and legal argument on contract interpretation. Court proceedings can be protracted compared with arbitration, but they provide formal judicial review and precedent-setting decisions that clarify legal principles. Parties should prepare comprehensive evidentiary records and consider expert reports to substantiate technical insurance claims. Courts remain a central route for final enforcement when arbitration or administrative remedies are inadequate or inapplicable.
What Are Policyholders’ Rights Under Lebanese Consumer Protection Laws?
Policyholders enjoy rights to clear pre-contractual disclosure, fair contract terms, timely claims handling, and remedies for misleading or abusive practices under consumer protection regimes that intersect with insurance regulation. These protections require insurers to provide transparent policy terms, explain exclusions, and process claims without undue delay; breach of these duties can trigger regulatory enforcement or civil remedies. Policyholders should keep policy documents, communications and claim records to support complaints or litigation. Being proactive about documentation and understanding statutory protections strengthens a policyholder’s position when pursuing remedies.
How Can Policyholders File Claims and What Are Their Legal Remedies?
Filing claims requires adherence to policy notice periods, submission of required documentation (police reports, medical records, invoices), and following insurer procedures for claims verification and assessment. If a claim is delayed or denied, policyholders should use the insurer’s complaint procedures, escalate to the ICC if unresolved, and consider arbitration or court litigation as necessary. Remedies for unjustified denials include damages for breach of contract, enforcement of policy benefits, and in some cases compensation for bad-faith handling. A clear claims checklist, timely communication, and escalation plan help policyholders navigate disputes efficiently.
What Are the Current Trends and Challenges in the Lebanese Insurance Market?
The Lebanese insurance market in 2025 faces headwinds and structural shifts: macroeconomic pressures such as inflation affect premium adequacy and renewal behaviour, reinsurance market retrenchment and political-risk concerns influence availability and pricing for certain covers, and insurtech adoption is reshaping distribution and claims processing. These trends create both risks like coverage gaps or rising costs and opportunities for improved digital servicing and product innovation. Stakeholders should monitor market indicators, reassess coverage limits and indexation clauses in light of inflation, and explore digital tools to improve access and claims speed in an evolving regulatory environment.
How Does Hyperinflation and Political Instability Affect Insurance Demand?
Hyperinflation erodes purchasing power, prompting policyholders to reduce cover, defer renewals, or demand policy terms that preserve real value through indexation or alternative currencies, which in turn strains insurer solvency modeling and premium adequacy. Political instability can increase demand for certain risk covers while depressing commercial activity that reduces premium bases in other lines. Policyholders should review limits and consider indexation clauses, reevaluate asset valuations, and work with insurers to structure sustainable premium arrangements that preserve coverage in real terms. Proactive risk assessment and contract review help mitigate the impact of macroeconomic volatility.
What Is the Impact of War Risks and Reinsurance Withdrawals?
War-risk exposures and reinsurance market withdrawals can reduce the availability of coverage for political violence, elevate premiums for affected lines, and lead insurers to apply exclusions or stricter underwriting terms. Businesses reliant on international reinsurance may encounter higher retention levels or difficulty renewing policies for high-risk perils. Practical mitigations include detailed contract review of exclusions, exploring alternative risk-transfer mechanisms, and enhancing loss-prevention measures to reduce exposure. Insureds and brokers should engage early with insurers to identify viable coverage strategies amid constrained reinsurance capacity.
How Is Insurtech Shaping the Lebanese Insurance Sector?
Insurtech adoption is improving distribution, underwriting efficiency, and claims processing through digital platforms, automated underwriting, and data-driven risk assessment, offering faster policy issuance and enhanced customer experiences. These technologies enable better price transparency and streamlined service for consumers while presenting regulatory considerations around data protection and digital governance. Consumers and intermediaries should assess insurtech solutions for their ability to improve access and transparency and verify that digital platforms comply with regulatory and data-security expectations. Insurtech can be a significant force for modernization when aligned with supervisory requirements.
What Are the Market Growth Forecasts and Regulatory Modernization Efforts?
Recent market commentary suggests cautious growth prospects contingent on macroeconomic stabilization and regulatory modernization initiatives that aim to strengthen solvency rules and consumer protection frameworks. Regulatory modernization efforts focus on updating solvency frameworks, enhancing supervisory capacities, and facilitating digital transformation while preserving consumer safeguards. For insurers and policyholders, modernization can improve market stability and product transparency, but stakeholders should monitor reforms and adapt governance, pricing models, and product designs accordingly. Active engagement with regulators and industry bodies supports a smoother transition as modernization progresses.
At The Guardian Insurance, we’re here to help you navigate your insurance needs. Explore our product and contact pages to request quotes or discuss compliance. Our representatives are ready to provide tailored guidance, evidence of compliance, and assistance in matching legal obligations to suitable coverage.
Conclusion
Understanding Lebanon’s insurance laws empowers individuals and businesses to navigate their rights and obligations effectively, ensuring compliance and protection. By familiarizing yourself with the regulatory framework, you can make informed decisions about necessary coverage and dispute resolution options. Explore the comprehensive offerings from The Guardian Insurance to find solutions that align with your legal requirements. Take the next step towards securing your financial future by reviewing our servcies pages today.




